What is a labral tear in the shoulder?
The labrum is a dense and fibrous cartilage attached anteriorly (front) and posteriorly (back) within the shoulder joint. This cartilage supports the shoulder joint by reinforcing the muscles and tendons of the rotator cuff and serves as a ligament attachment site. There are many ways in which the labrum can become damaged: 1) can become completely detached from the bone with a shoulder dislocation; 2) the latticework structure of the fibrous connective tissue can become torn and commonly seen among the older population; and, 3) the biceps tendon can be partially or completely torn from its labral attachment site. Because of the various degrees and mechanisms of a labral tear, it is important to seek appropriate treatment from an orthopedic shoulder specialist. Dr. Answorth A. Allen, MD, an orthopedic shoulder specialist serving patients in Manhattan, New York City, Westchester, Long Island and surrounding areas, has the knowledge and understanding, as well as substantial experience in treating patients who have experienced a labral tear.
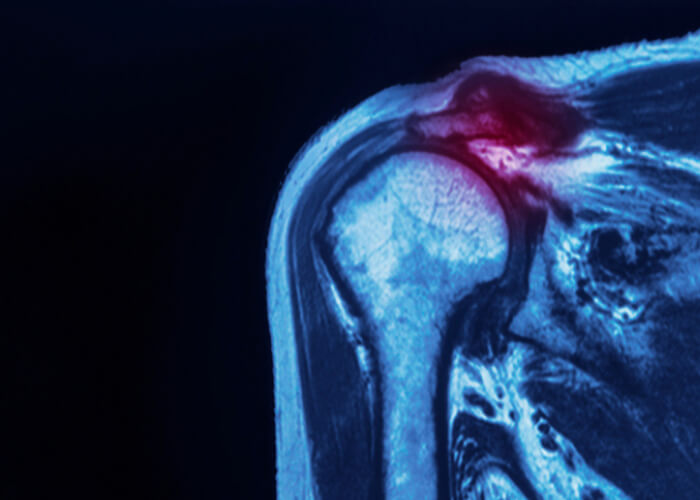
What is a SLAP tear in the shoulder?
The superior (top) portion of the shoulder labrum serves as the biceps tendon attachment site. In the event of an injury, this attachment site as well as the anchoring points of the shoulder labrum can be affected and is known as a Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior (SLAP) tear. This type of injury is often seen among athletes that perform repetitive overhead movements in sports like tennis and baseball. A SLAP tear can also be the result of a traumatic injury, a motor vehicle collision, or bracing a fall with an outstretched arm.
What are the symptoms of a labral or SLAP tear?
If a labral or SLAP tear is suspected, it is important to consult an orthopedic shoulder specialist as the symptoms of a labral or SLAP tear coincide with a number of shoulder conditions. Shoulder pain worsened with lifting heavy objects or overhead shoulder motions is the most common complaint of a labral or SLAP tear. Other symptoms can include:
- Decreased range of motion and shoulder strength
- Dislocated shoulder
- Shoulder instability
- A grinding, popping, or clicking sensation within the shoulder joint
How are labral and SLAP tears diagnosed?
Dr. Allen will obtain a comprehensive medical history and perform a thorough physical examination to include an assessment of the shoulder’s range of motion, strength, and stability. Diagnostic imaging, such as x-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be needed to identify any damage to other structures within the shoulder and confirm a labral or SLAP tear diagnosis. In addition to an MRI, Dr. Allen may request an arthrogram, an imaging technique that utilizes intravenous dye to determine if the blood supply within the shoulder joint has been compromised.
What is the treatment for a labral or SLAP tear?
Non-surgical treatment:
Conservative treatment options are often all that is needed to successfully resolve a labral or SLAP tear. A combination of rest, ice, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications may be used for pain management. If the pain is not well-controlled with oral medications, Dr. Allen may prescribe stronger pain medications to be taken as directed. When the pain has dissipated, a physical rehabilitation program to restore shoulder strength and range of motion may be recommended.
Surgical treatment:
In the event of severe labral and SLAP tears, or if conservative therapy is unsuccessful, surgical intervention may be necessary. Dr. Allen may recommend a shoulder arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure using a small camera (arthroscope), to visualize the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the shoulder joint. Based upon the intra-operative findings with a shoulder arthroscopy, Dr. Allen can determine the best repair option among the following techniques:
SLAP repair. This surgical method attaches the torn labrum to the shoulder joint with special surgical anchors that are secured within the bone. This is a routine surgical approach for younger patients that would like to remain physically active.
Debridement. The simplest of these procedures, debridement removes the torn or frayed portions of the labrum. This approach is reserved for patients with small labral tears that do not involve the biceps tendon.
Biceps tenodesis. This surgical technique is recommended for severe SLAP tears that involve the biceps tendon. This procedure separates the biceps tendon from its attachment site on the labrum, the damaged portion of the tendon is excised, and then the repaired tendon is reattached to the humerus (upper arm bone) with special surgical anchors that are secured within the bone.
Labrum Tear Specialist

A labral tear occurs when there is damage to the cartilage supporting the shoulder and rotator cuff. This injury can occur in many different ways and varies in severity. In most cases, a labral tear can be treated conservatively with therapies and rest. More severe cases, however, may require surgery. Shoulder expert Doctor Answorth Allen is experienced in diagnosing and treating this intricate injury for patients in Manhattan, New York City, Westchester, Long Island and surrounding areas who have experienced a labral tear. Contact Dr. Allen’s team today!






